Blockchain Industry – Innovation or Overhyped
Blockchain industry, and the modern-day technological innovation that drives it can be the next big leap we need to "fix" the Internet, but the question still stands:
"What is the Blockchain?"
We say "can" because the technology is still in an unknown territory and you could just be the Christopher Columbus of blockchain solutions.
This blog will be a brief tutorial on this technology, its constant evolution in the industry, and the uses we have found for it so far.
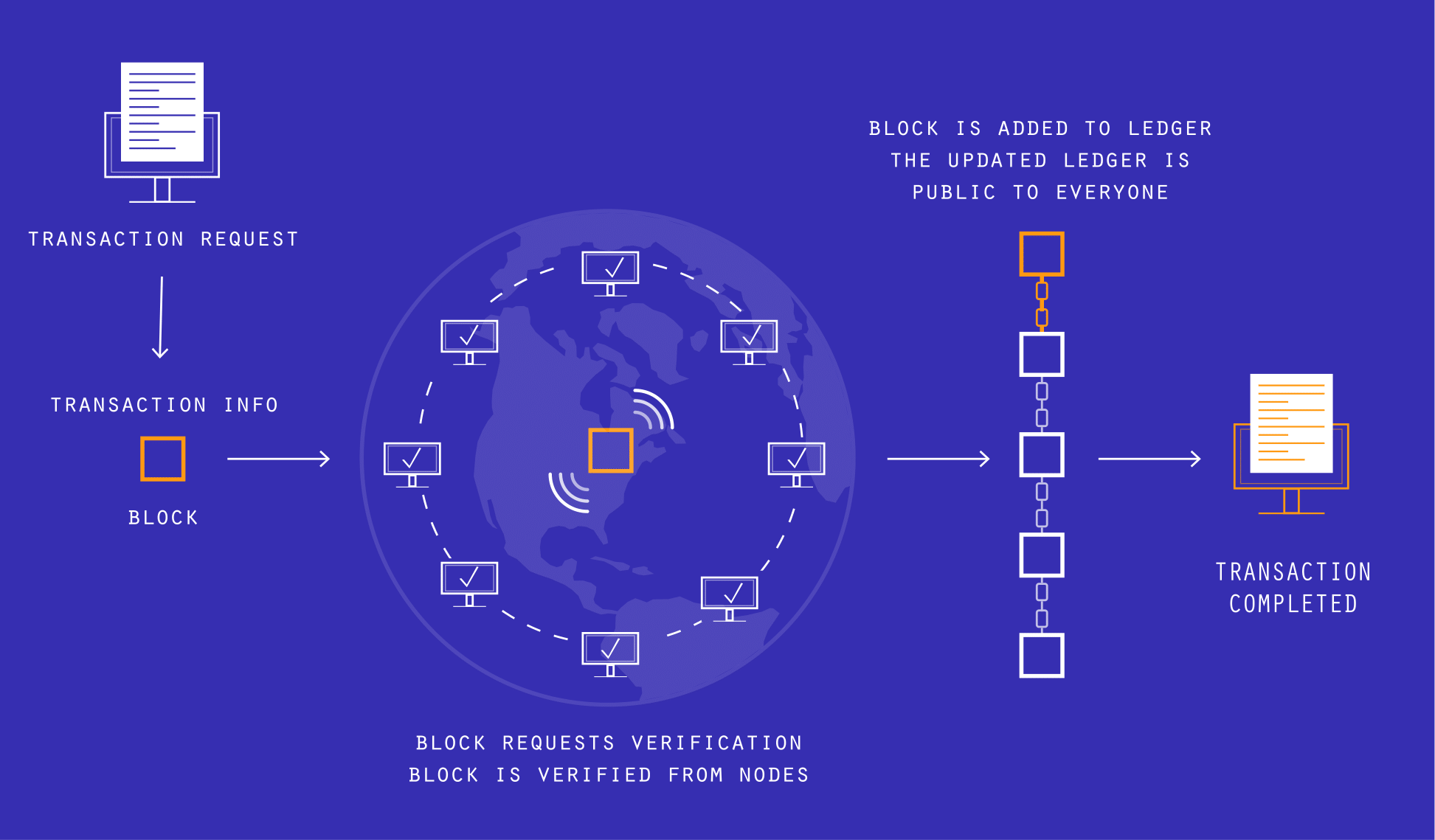
What is Blockchain Technology?
The term is fairly simple, it is a block of chains that form a database. This idea was used to create a digital ledger of transactions that were shared in a network of computers known as "nodes". What this meant was that every person in that network had a copy of the ledger, and they could view that whenever they pleased.
This constantly-updated, decentralized ledger allowed for greater safety, seeing as the ledger was easily-verifiable. No centralized database meant that you couldn't just simply access any single database and change anything.
To summarize Blockchain - an incorruptible, transparent database-building technology.
Use Cases in the Blockchain Industry
The technology has the ability to transform a wide array of industries with the simple idea of a secure, decentralized, immutable database.
Namely, some of the industries that have found a use for the technology so far are:
- Financial Services
- Smart Contracts
- Identity Management
- Cloud Storage
To explain how those industries have utilized the technology, we will take first-hand examples of companies that have applied blockchain to make their ideas possible.
Financial Services
In account to the technology being immediately associated to Bitcoin, it wasn’t a surprise that one of the first applications for it was in the financial services - banks.
The key features to mention here are:
- Security
- Transparency
- Immutability
- Cost-efficiency
Banks are currently the first major corporations trying to transition to the digital ledger, and with companies like R3 completing proof-of-concepts with eleven banks and we are slowly transitioning from ideas to real-world applications.
Not to say that this technology will completely change the way we think of banks, the technology will simply augment on the present infrastructure of banks.
The way blockchains can, and will eventually, contribute is by changing the way we deal with intermediary transactions(by removing the need for a lot of them), the speed of the transactions, and most importantly - the cost.
Although it is still in infancy, the proof-of-concepts that have been developed so far in the “Financial Services” department is providing a promising future. If you want to find out more about this check out our blog for financial services and blockchain.
Smart Contracts
One of the first fresh ideas, on the seemingly-endless potential for this technology, was that of Smart Contracts, notably Ethereum.
A “Smart Contract” is the digitalization of the traditional approach to contracts. A method that can enforce a contract simply through the blockchain. The contract is given the terms and those terms are saved as instructions inside the code, and presto, you have a smart contract.
“What does this mean for us?”
Besides the obvious, which is, a quicker way of formulating a contract, it also means removing the need for the middle-man.
The contract can also be enforced much more easily because of the penalization that will occur from the agreements already set. The traditional approach to contracts heavily relies on a third-party, like the judicial system, to enforce the agreements, which is very time-consuming and cumbersome.
Identity Management
Identity Management (IDM) works on the basis of how a person gains identity on the network and the technologies that are set around securing that identity.
It deals with giving access to the right person at the time of the request, but the question is:
“How do we know who the right person is?”
The digital ledger could be one of the leading successors in the Identity Management industry.
A prime example is a startup called “ShoCard”, which attempts to solve the issue through the use of public and private keys side-by-side with your information being hashed, and using multi-factor authentication.
ShoCard has managed to create a very slick and powerful application using the technology,
This company proves that the blockchain industry isn’t silently sleeping, and is actively looking to disturb many more industries.
With the constant development and improvement of blockchain technology to support more and more Transactions Per Second(tps), and with companies like BlockCypher, who, through the decentralized ledger, built a whole system to support API building, which now supports more than 2 million API calls per day, the limits of Blockchain look like they aren’t going to stretch out for a while.
Cloud Storage
Another perfect example of the variety of this industry and the application of the technology; StorJ is an open-source, decentralized cloud storage that uses the distributed ledger of blockchain technology.
“But how can it be open-source if there are no central databases?”
It goes back to the original premise of Bitcoin through the use of “miners”, but Storj calls them “farmers”.
Farmers allocate unused disk space to StorJ and they get paid a rent of proprietary cryptocurrency for their contributions.
The security concerns with this are minimal, due to the fact that the files are fragmented and distributed across the nodes, never sharing one complete file on a single computer.
The shards are immutable when saved inside the blockchain and tempering from farmers cannot happen.
Anyone concerned with security can rest knowing their files are safe, but also knowing that Storj provides redundancy for files through copying and pasting them as different shards.
Blockchain Solutions are Blooming
This industry is ever-growing. The technology may seem scary at first, but the premises on which it stands make it a desirable technology to implement. True, it does suffer from “technological infancy” which can make investors hesitant at first, but that does not make it any less powerful than it is.
The technology is open-source, making it available for anyone and everyone.
Stick your nose in the industry, you might find uses for it, or create your own use for it; the possibilities look endless.